Intrinsic value fair value stock options
Stock market options give option holders rights to buy or sell shares at a certain price. Uniquely, options have expiration dates that put a time limit on those rights. The fair value of an option is the mathematical calculation of the value of those rights based on price volatility and the time remaining on the clock.
Due to Wall Street savvy and software, the current market price of an option is a close approximation of the fair value.
Option time value - Wikipedia
The market price -- as stand-in for fair value -- of an option can be divided into intrinsic value and time premium.
Look up the current details and price information on a trading stock option. The important facts are the type of option -- put or call -- the strike price and the current share price of the underlying stock.
The expiration date is built into the option price and so is not relevant for this exercise. The strike price of an option is the stock price at which an option holder will buy -- for call options -- or sell -- for puts -- if the option is exercised. Determine the "moneyness" of the option contract.

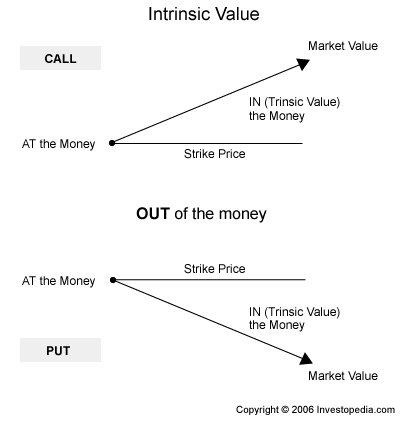
The more correct term for an option with intrinsic value is "in the money. A put option is in the money if the stock is below the put's strike price. If the option is out of the money, the entire price or premium of the option is time premium, and there is no intrinsic value.
Calculate the amount of intrinsic value of a call option by subtracting the option strike price from the current stock price. Calculate the intrinsic value of a put option by subtracting the current share price from the option strike price. The remainder of the cost of the put option is the time premium.
Trading action keeps option prices in line with theoretical fair values. Tips The intrinsic value of the option is the amount of money you would make by exercising the option and simultaneously selling -- call options -- or buying -- put options -- the underlying stock.
The time premium portion of an option's value is the worth of the rights given to the option buyer by the terms of the contract. If the stock price is equal to an option's strike price, the option is said to be "at the money" -- neither in or out of the money. At-the-money options have no intrinsic value.
The fair value calculation of an option comes from a mathematical model that uses historical data to project a future value. What Happens When a Stock Put Expires?
Difference Between Market Value and Intrinsic Value Can I Hedge a Call Option With a Put Option? How to Take Advantage of Theta Decay in Options How to Calculate a Stock Option Break-Even Point Risk Factors Affecting Option Price. How to Trade Leveraged Stock Options How Does a Put Option Work? The Variables That Drive a Stock Option's Value.
Intrinsic Value Vs. Fair Market Value Method | eHow
How to Make Consistent Returns With Options What Does It Mean to Exercise Stock Options? Tradable Stock Options What Happens to a Stock Option if It Is Expired and You More Articles You'll Love.
How to Trade Leveraged Stock Options. How Does a Put Option Work?
Intrinsic Value
How to Make Consistent Returns With Options. What Does It Mean to Exercise Stock Options?
What Happens to a Stock Option if It Is Expired and You Don't Exercise It? Difference Between Market Value and Intrinsic Value.
Can I Hedge a Call Option With a Put Option? How to Take Advantage of Theta Decay in Options. How to Calculate a Stock Option Break-Even Point. Risk Factors Affecting Option Price.
No Longer an Option
How to Trade Options in a Bear Market. About Us Careers Investors Media Advertise with Us Check out our sister sites. Privacy Policy Terms of Use Contact Us The Knot The Bump.